Understanding Your Digestive System
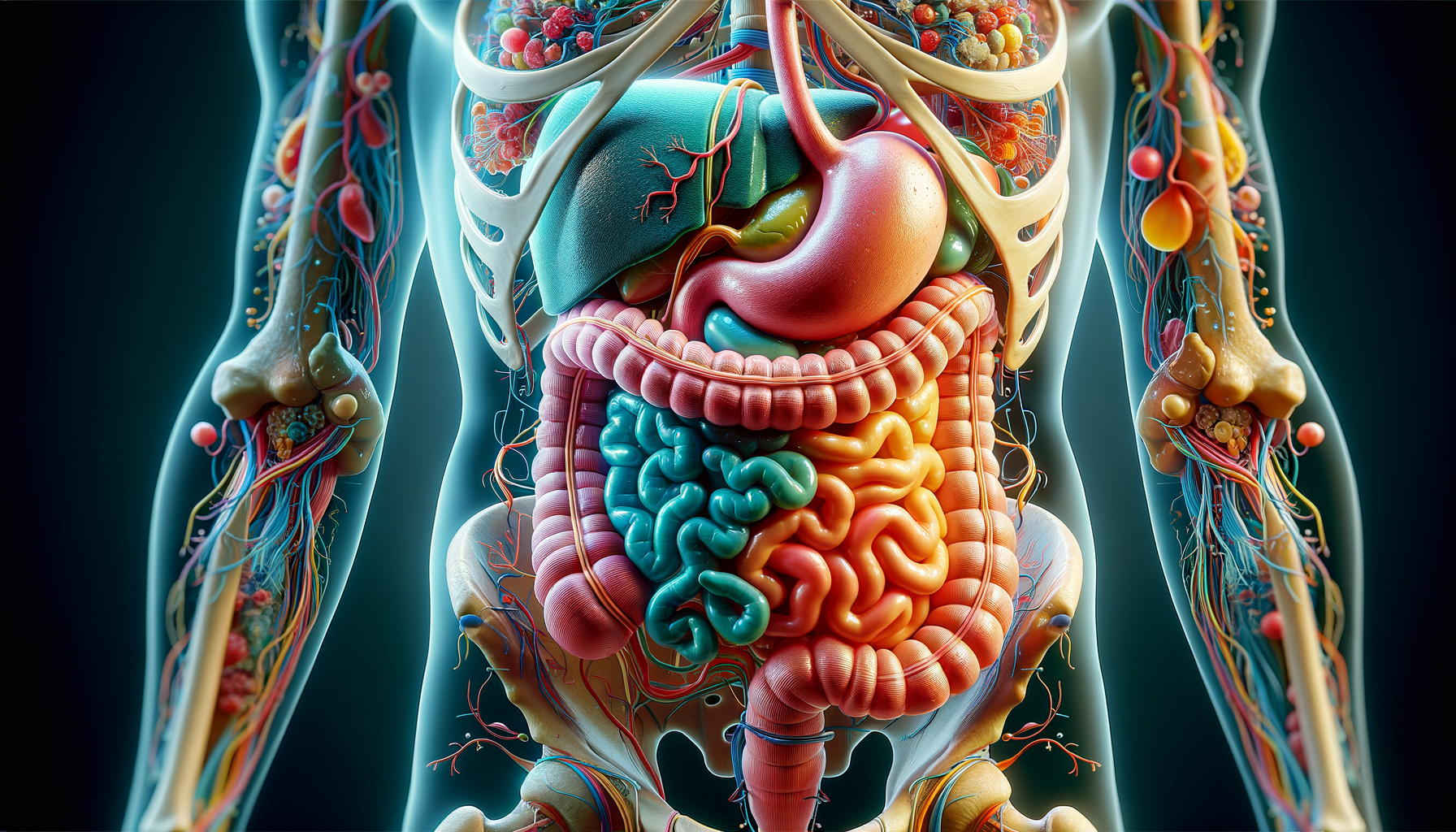
The digestive system is a complex network of organs that work together to convert food into energy and essential nutrients. This system begins at the mouth and ends at the anus, involving several key organs such as the stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas. Each organ plays a distinct role in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and expelling waste.
To appreciate the intricacies of the digestive process, consider the journey of a simple meal. It starts with chewing, where enzymes in saliva initiate the breakdown of carbohydrates. As the food travels down the esophagus, it reaches the stomach, where gastric acids further dissolve it. The partially digested food then moves to the small intestine, where most nutrient absorption occurs. Finally, the large intestine absorbs water and forms waste for elimination.
Understanding the digestive system is fundamental for identifying potential health concerns. For instance, if nutrient absorption is impaired, it could lead to deficiencies and related health issues. By learning how the digestive system operates, one can better recognize symptoms indicating digestive disorders, such as bloating, constipation, or diarrhea.
Common Digestive Health Concerns
Digestive health issues are prevalent, affecting millions worldwide. Some of the most common concerns include:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Celiac disease
- Constipation and diarrhea
GERD is characterized by acid reflux, where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation. IBS, on the other hand, is a functional disorder marked by abdominal pain and altered bowel habits. IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, involves chronic inflammation of the digestive tract.
Understanding these conditions is vital for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. For example, dietary changes, stress management, and medication can help alleviate symptoms of IBS. Meanwhile, individuals with celiac disease must adhere to a strict gluten-free diet to prevent adverse reactions.
Role of Nutrition in Digestive Health
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in maintaining digestive health. A balanced diet rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals supports the digestive system’s function and overall health. Fiber, found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, is essential for promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
Probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods like yogurt and kefir, can also enhance digestive health by maintaining a healthy gut microbiota. These microorganisms aid in digestion, boost immunity, and may even improve mood and mental health.
On the other hand, excessive consumption of processed foods, high sugar, and unhealthy fats can disrupt digestive health, leading to conditions such as obesity, GERD, and IBS. Therefore, making informed dietary choices is crucial for sustaining a healthy digestive system.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Digestive Health
Beyond diet, several lifestyle factors significantly impact digestive health. Regular physical activity, for instance, stimulates intestinal activity, helping to prevent constipation and maintain a healthy weight. Stress management is equally important, as chronic stress can exacerbate digestive disorders and lead to symptoms like indigestion and stomach ulcers.
Hydration is another critical aspect, as water aids digestion by dissolving nutrients and waste, facilitating their passage through the digestive system. Additionally, adequate sleep supports the body’s ability to repair and maintain healthy digestive function.
By integrating healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can enhance their digestive health and overall well-being. This holistic approach not only addresses symptoms but also targets the root causes of digestive issues.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many digestive issues can be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter remedies, some symptoms warrant professional medical evaluation. Persistent or severe symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, blood in the stool, or severe abdominal pain should not be ignored.
Consulting a healthcare provider is crucial for obtaining an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Healthcare professionals can conduct tests, such as endoscopies or blood tests, to identify underlying conditions and recommend targeted interventions.
Early intervention can prevent complications and improve outcomes, highlighting the importance of seeking medical advice when necessary. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can take charge of their digestive health and enhance their quality of life.



Leave a Reply