Understanding Foot Nerve Discomfort
Foot nerve discomfort, often described as tingling, numbness, or a burning sensation, can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. This condition, medically known as peripheral neuropathy, involves damage to the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord, particularly those in the feet and hands. The sensations can range from mildly irritating to profoundly debilitating, depending on the severity and underlying cause.
Peripheral neuropathy in the feet can be attributed to various factors. Common causes include diabetes, which is one of the leading contributors due to prolonged high blood sugar levels damaging the nerves. Other causes can include traumatic injuries, infections, metabolic problems, and exposure to toxins. In some cases, the cause remains idiopathic, meaning it is unknown. Recognizing these symptoms early is essential for effective treatment and management.
Foot nerve discomfort is not just a physical ailment but can also lead to emotional distress. The constant pain or discomfort can hinder daily activities, leading to frustration and even depression. Understanding the underlying causes is the first step in addressing this condition, enabling individuals to seek appropriate medical advice and support.
Common Causes of Foot Nerve Discomfort
Several factors can lead to foot nerve discomfort, each with distinct mechanisms and implications. Diabetes is the most prevalent cause, with diabetic neuropathy affecting nearly 50% of those with diabetes over their lifetime. The high levels of glucose in the blood can lead to nerve damage, particularly in the extremities.
Other causes include:
- Alcoholism: Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to nutritional deficiencies, particularly of B vitamins, essential for nerve health.
- Infections: Certain viral and bacterial infections, such as Lyme disease and shingles, can cause nerve damage.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can lead to nerve inflammation and damage.
- Inherited disorders: Genetic conditions like Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease can affect the peripheral nerves.
Understanding these causes is crucial for diagnosis and treatment. Identifying the root cause can help tailor a treatment plan that addresses not only the symptoms but also the underlying issue, providing more comprehensive relief.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of foot nerve discomfort can vary widely, depending on the cause and severity of the nerve damage. Common symptoms include tingling or numbness in the feet, a sharp or burning pain, a feeling of extreme sensitivity to touch, and muscle weakness. In severe cases, individuals may experience a loss of coordination and balance, making walking difficult.
Diagnosing foot nerve discomfort involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Doctors may perform nerve conduction studies or electromyography to assess the electrical activity in the nerves and muscles. Blood tests can also help identify underlying conditions such as diabetes or vitamin deficiencies.
Early diagnosis is essential for effective management, as it allows for interventions that can slow or halt the progression of nerve damage. Patients are encouraged to report symptoms to their healthcare provider as soon as they occur to facilitate timely diagnosis and treatment.
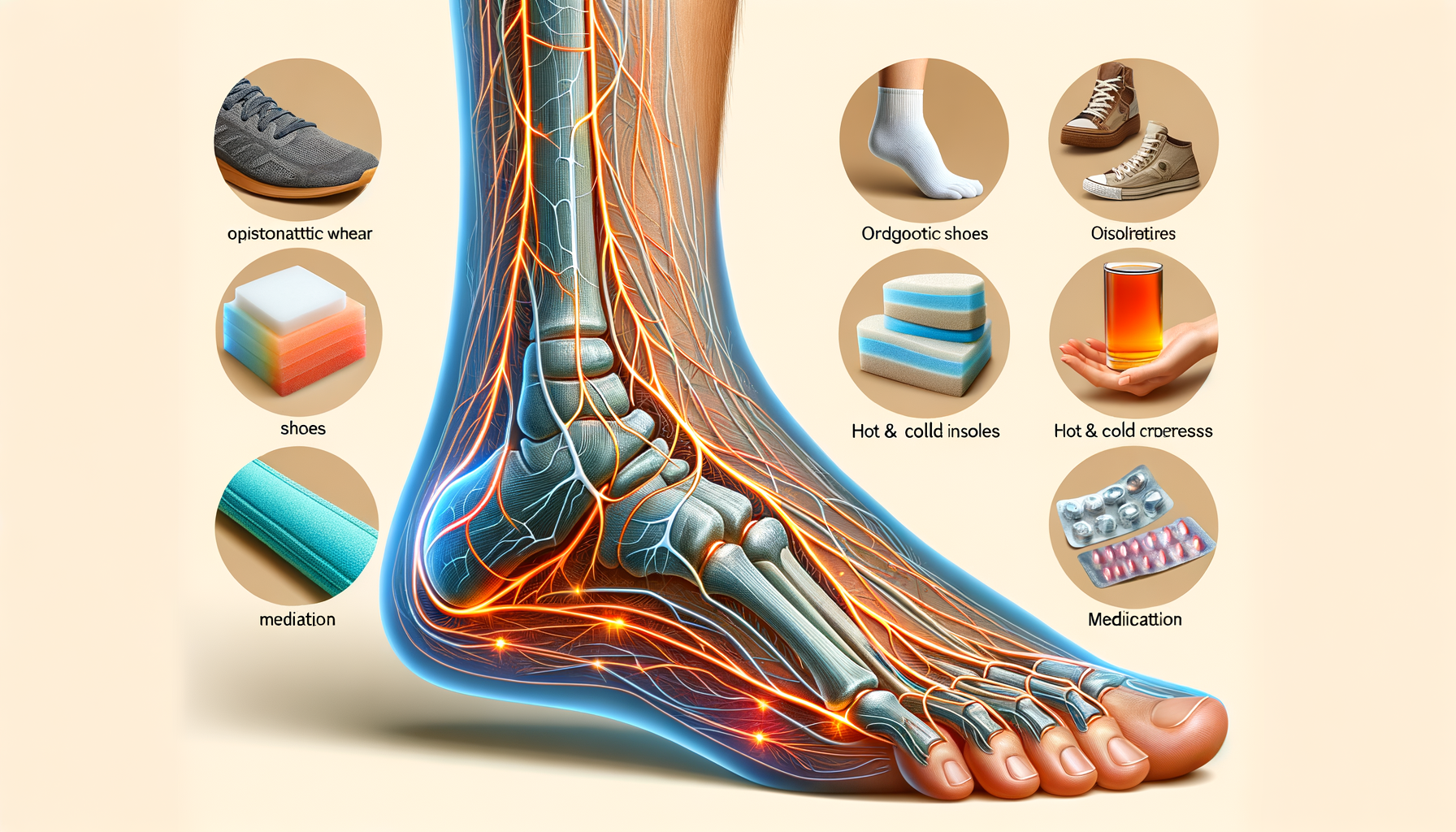
Support Options for Managing Foot Nerve Discomfort
Managing foot nerve discomfort involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and supportive therapies. Medical treatments may include medications to manage pain and inflammation, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or prescription medications like anticonvulsants and antidepressants that can help alleviate nerve pain.
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing symptoms. Regular exercise can improve blood flow to the nerves and reduce discomfort. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly B vitamins, is also crucial for nerve health. Patients with diabetes should closely monitor their blood sugar levels to prevent further nerve damage.
Supportive therapies such as physical therapy can help maintain muscle strength and improve coordination. Some individuals find relief through complementary therapies like acupuncture or massage, which can help alleviate pain and improve overall well-being.
Long-Term Management and Outlook
Long-term management of foot nerve discomfort requires ongoing care and attention to prevent further nerve damage and improve quality of life. For those with chronic conditions like diabetes, maintaining strict control of blood sugar levels is paramount. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can help monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Individuals are encouraged to adopt a proactive approach to their health, focusing on preventive measures and early intervention. This includes wearing appropriate footwear to protect the feet, avoiding activities that may exacerbate symptoms, and engaging in regular physical activity to promote nerve health.
While foot nerve discomfort can be a challenging condition, many individuals find that with the right combination of treatments and lifestyle adjustments, they can lead fulfilling lives. Support from healthcare providers, family, and community resources can provide the necessary encouragement and assistance in managing this condition effectively.



Leave a Reply